神经干细胞(NSCs)是具有分化为神经细胞及胶质细胞潜能,并具有自我更新能力的一类细胞,其不同的生理阶段具有不同的代谢状态。本研究基于实验室已发展的薄膜铂热电阻温度传感器 (Cai Li, et al. IEEE transactions on Biomedical Engineering 2019, 66(7), 1898-1904.),并结合3D打印技术,搭建了无线多通道温度测量系统,用于检测神经干细胞贴壁生长和增殖过程的温度,实现无损检测5000数量级的神经干细胞群温度变化,监测时间超过24小时,温度检测精度为0.05℃。
通常,成体细胞依赖于线粒体氧化磷酸化作为三磷酸腺苷(ATP)生成的主要来源。 相反,NSC很大程度上取决于糖酵解能量的产生。研究表明,外部温度可调节细胞的生长和发育。通过在细胞水平研究其温度变化可实现干细胞生长、增殖以及分化等行为的更全面分析。因此,进一步实验中使用了甲状腺激素(T3)对神经干细胞进行干预,结果表明,T3对干细胞生长和增殖过程具有显著的温度变化影响,且存在浓度依赖的特性,为应用于贴壁细胞在正常培养或药物作用下的温度检测提供了新的思路和手段。
该研究开发的系统可适用于评估各种细胞的热反应,检测增殖和分化过程中干细胞的代谢状态。可为将来检测电、磁、光、声刺激下各种细胞生理反应提供温度变化的参考信息。
该论文于2020年2月5日在线发表在Analytical chemistry杂志上(Jiaxu Ding, Jing Li, Fang Yang*, Ning Gu*. A Multi-Channel System for Temperature Sensing of Neural Stem Cells in Adherent Culture. Anal. Chem. 2020, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b05134.
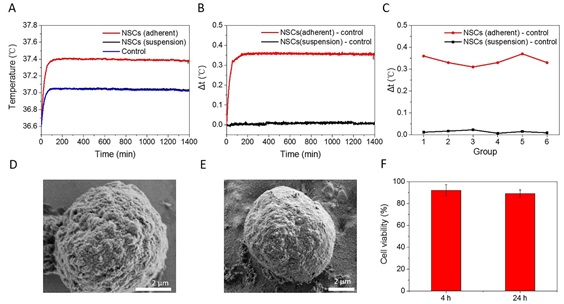
Figure. Temperature of NSCs. (A) Temperature of suspended NSCs and adherent NSCs. (B) Temperature difference (Δt) of suspended NSCs and adherent NSCs. (C) Temperature difference (Δt) of repeated experiments. (D) Morphology of normal NSCs under SEM. (E) Morphology of NSCs after temperature detection. (F) During the temperature measurement, the viability of neural stem cells was 92% and 89% after 4 h and 24 h measurement.
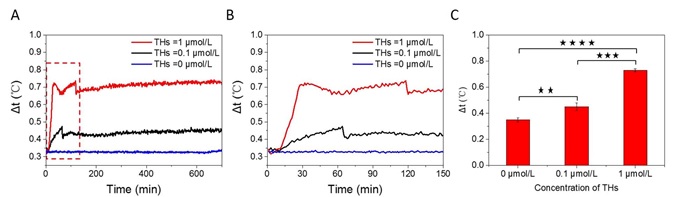
Figure. Effects of THs on the temperature of NSCs. (A) Changes in the temperature of NSCs stimulated by different concentrations of THs (0, 0.1, and 1 µmol/L). (B) Changes in the temperature of NSCs in the first 150 min. (C) Statistical results of temperature difference, the specific values are: 0 µmol/L-0.33°C, 0.1 µmol/L-0.45°C, 1 µmol/L-0.72°C.