金属纳米颗粒聚集体的光学性质非常复杂,个体颗粒的材质、几何结构以及空间排列都会影响等离激元的耦合。由于金属纳米颗粒可以看作一个耦合谐振子,而量子力学的共振和干涉有着类似的数学表达,因而等离激元耦合产生了许多量子物理中常见的现象,如 FANO 共振、电磁诱导透明 (EIT)、Rabi分裂等,理解其中的物理机制,控制等离激元的耦合实现特定的功能,是等离激元光子学的一个主要任务。本文基于CDA理论提出了定性估计纳米颗粒聚集体光学散射特性的散射分解方法,可以将寡聚体等离激元的二维耦合简化为两步一维耦合,从而可以方便地预测纳米颗粒寡聚体的光学性质,为等离激元耦合的人工调控提供了有力的理论工具。
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jp4004054
Meng Wang , Min Cao , Zhirui Guo , Ning Gu,Two-Step Decomposition of Plasmon Coupling in Plasmonic Oligomers, J. Phys. Chem. C, DOI: 10.1021/jp4004054 2013.
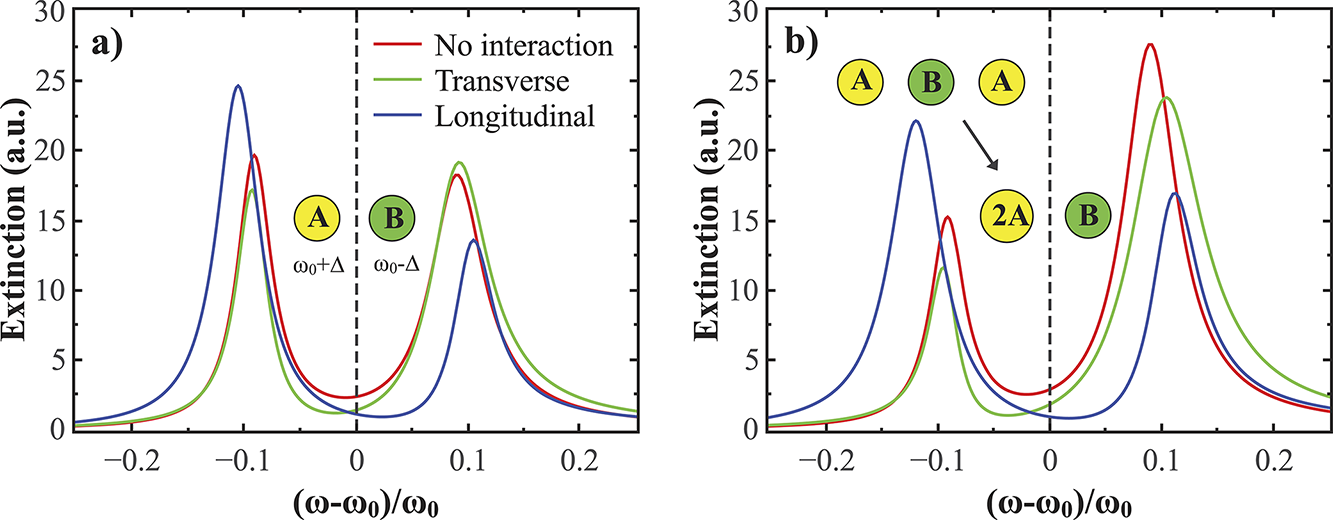
Figure 1. Calculated extinction spectra of a heterogeneous dimer (a) and trimer (b) under transverse and longitudinal excitations by CDA. Thecolors of the sphere indicate the type of the plasmonic particles.
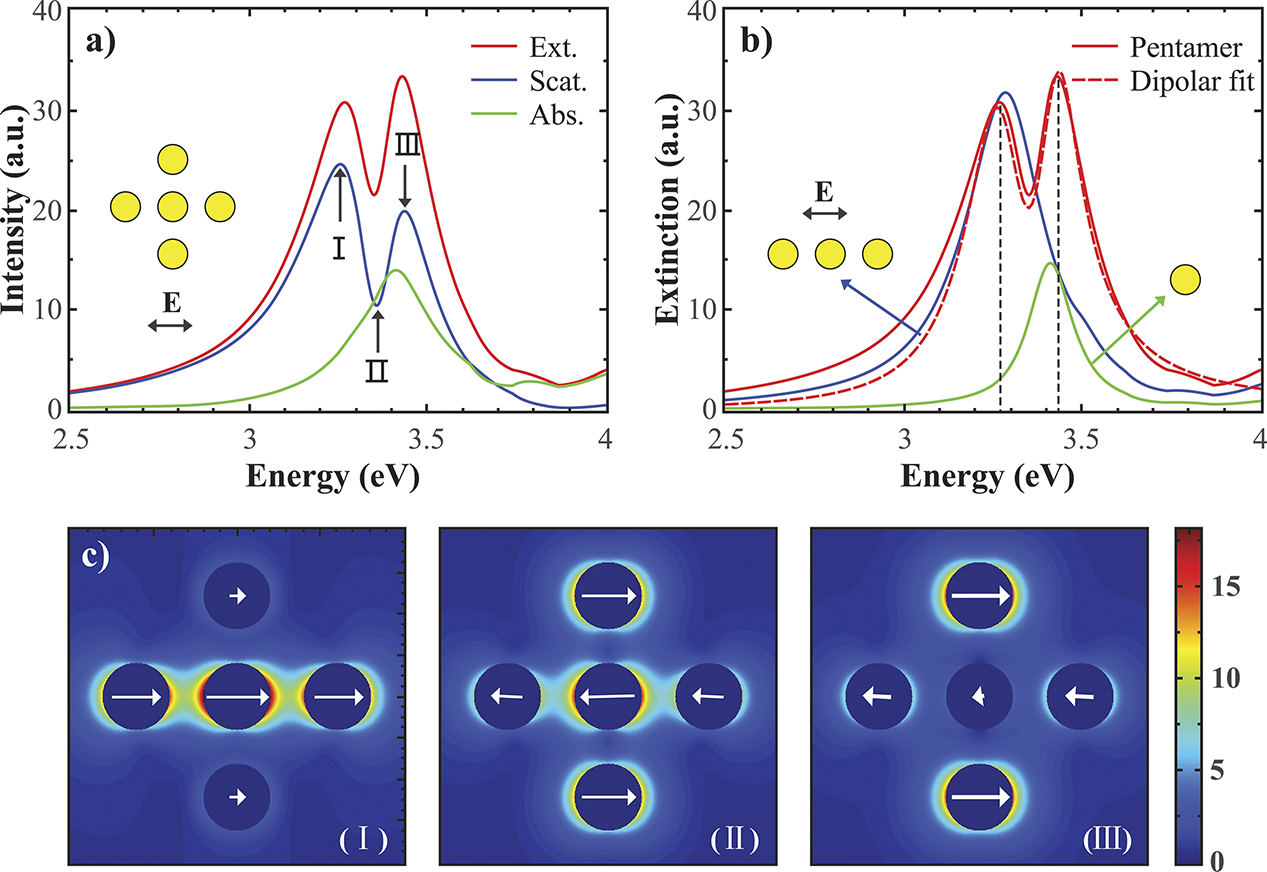
Figure 2. (a) Extinction, scattering and absorption cross sections of a pentamer by dynamic CDA, the pentamer consists five silver nanoparticles (a =25 nm) with gap size g = 25 nm. (b) Decomposition and dipolar fit of scattering spectrum for the pentamer. (c) Near field distributions at three specific frequencies as marked in (a).
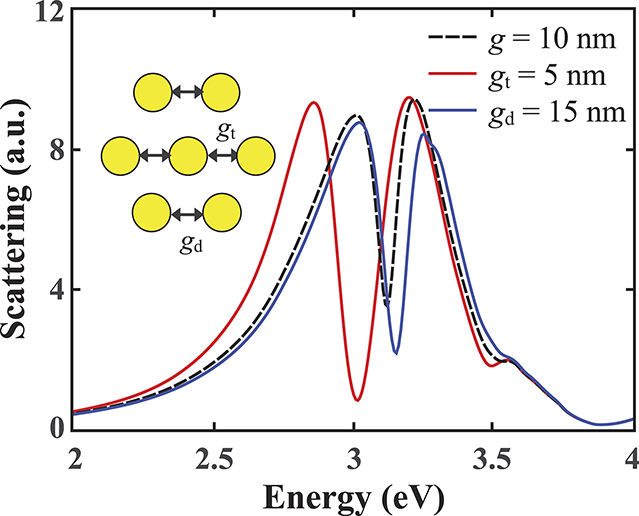
Figure 4. Tuning of plasmon resonance of silver heptamer. The dashed line corresponds to the scattering cross section of the heptamer with gap size of 10 nm.