微气泡在较高声压(>0.1MPa)超声辐照下,由于剧烈的伸缩振动会发生破裂,导致微气泡周围的生物组织或细胞出现热效应、声穿孔或声辐照力等生物效应,这正是目前微气泡介导的超声无损治疗应用研究的基础。本研究以包裹Fe3O4纳米颗粒(86.47μg/ml)的微气泡为模型,建立了微气泡与SMMC-7721肝癌细胞的体外超声实验。首先,通过控制超声辐照参数(1MHz频率,不同声强,相同辐照时间),评价了微气泡中的Fe3O4纳米颗粒控制释放进入细胞的效率;然后,对被Fe3O4纳米颗粒标记后的细胞进行了磁共振成像研究;最后,通过对微气泡超声辐照后的细胞进行SEM形貌观察,以及细胞内钙流变化情况实验,探讨了微气泡携带的Fe3O4纳米颗粒在超声能量辅助下,进入细胞声穿孔方式和细胞发生的相关生物效应机理。 Fang Yang, Miao Zhang, Wen He, Ping Chen, Xiaowei Cai, Li Yang, Ning Gu, Junru Wu.Controlled Release of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles in Encapsulated Microbubbles to Tumor Cells via Sonoporation and Associated Cellular Bioeffects.Small 2011, 7(7), 902–910
Figure 6 . Cell viability exposed to US depends on the cell-cycle phase.
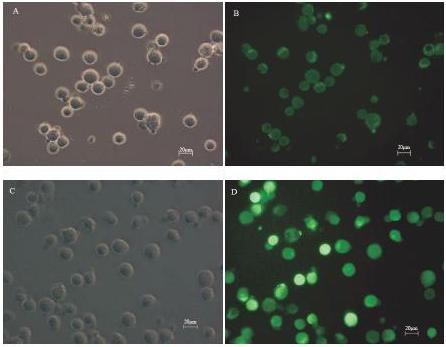
Figure 7. Typical images of SMMC-7721 cells after Fluo-3 staining (×100). (A) and (B) 7721 cells without the US and microbubbles treatment under the bright field and epifluorescent field; (C) and (D) 7721 cells after the US exposure (0.5 W cm-2) and nanoparticle-imbedded microbubbles treatment under the bright field and epifluorescent field.