本文建立了一种简单有效的方法制备聚乙二醇修饰的氧化铁纳米粒子。首先通过多个羧基与氧化铁纳米粒子的螯合作用,将聚丙烯酸(PAA)修饰到氧化铁纳米粒子表面,从而向氧化铁纳米粒子表面引入大量的羧基,再利用羧基与α,ω-二氨基PEG分子中一端氨基的反应,将PEG高密度的连接到氧化铁纳米粒子表面。该氧化铁纳米粒子具有良好的生物相容性和抗巨噬细胞吞噬能力。小鼠体内实验表明,PEG修饰可以有效降低氧化铁纳米粒子被肝脾组织摄取,从而实现其在肿瘤组织的有效富集,达到高效的磁共振肿瘤成像效果,该纳米粒子在磁共振肿瘤成像领域具有巨大的应用前景。
Dongfang Liu, Wei Wu, Jingjing Ling, Song Wen, Ning Gu,* Xizhi Zhang. Effective PEGylation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for High Performance in Vivo Cancer Imaging, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011,DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201001658.
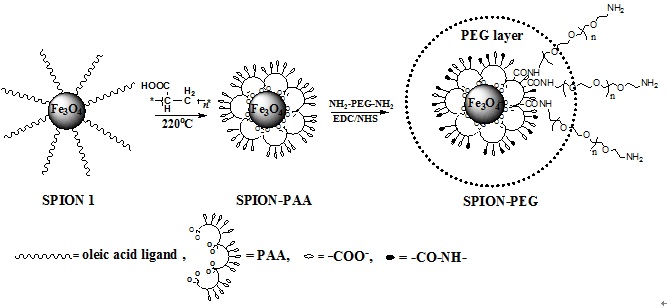
Scheme 1. Schematic chemical structures of SPION-PAA, SPION-PEG and the synthetic route.
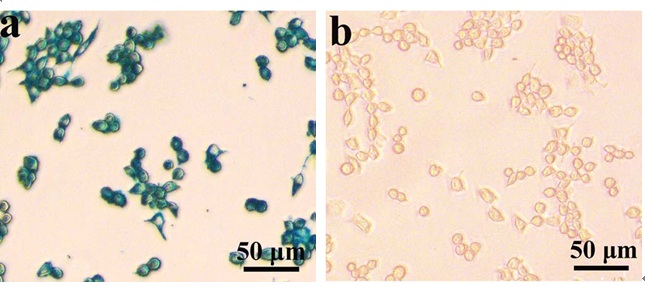
Figure 6. In vitro Prussian blue staining images of macrophages, RAW 264.7, after 2 h treatment with 0.6 mg Fe mL-1 of each SPIONs: SPION-PAA (a) and SPION-PEG (b).
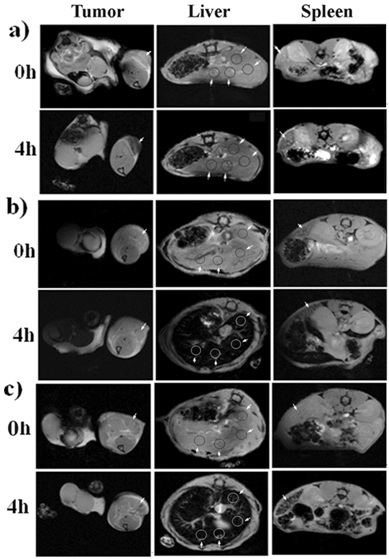
Figure 7. T2*-weighted images (TR/TE of 408 ms/3.5 ms) at pre-injection and 4 h post-injection of 4 mg kg-1 of SPION-PEG (a), SPION-PAA (b) and Resovist (c) in the regions of the tumor on the proximal thigh, liver and spleen of the mice.
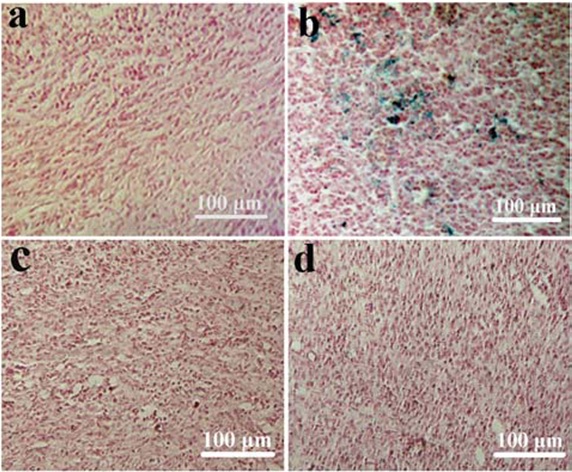
Figure 8. Ex vivo Prussian blue and nuclear fast red double staining images of tumor tissues excised from the mice untreated (a) and at 4 h post-injection of SPION-PEG (b), SPION-PAA (c) and Resovist (d) respectively.