药物控释系统由于能够提高药物的疗效和减少药物毒副作用以及减少给药次数,受到了国内外研究者的广泛关注,因此发展具有生物相容性和生物可降解的药物控释系统具有重要的意义。PLGA是FDA批准的可用于人体的高分子聚合物材料,广泛的应用于药物载体,但是PLGA的缓慢释放性能可能会导致肿瘤细胞的多耐药性。因此,开展有关PLGA药物载体的可控释放载药系统具有重要的研究意义。本文通过双乳化发结合LBL方法制备PLGA磁性载药微囊,观察了交变磁场作用下PLGA磁性载药微囊可控药物释放行为,并初步研究了该磁性载药微囊在交变磁场作用下对肿瘤生长的抑制作用。
Kun Fang, Lina Song, Zhuxiao Gu, Fang Yang, Yu Zhang, Ning Gu. Magnetic field activated drug release system based on magnetic PLGA microspheres for chemo-thermal therapy. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2015, 136: 712-720. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.10.014
文章链接:http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0927776515302459

Preparation of PLGA hollow microspheres decorated with IOs (MMS) and their feature.
A) Schematic showing the preparation of MMS. SEM and TEM image of MS (B, C, D) and
MMS (E, F, G).
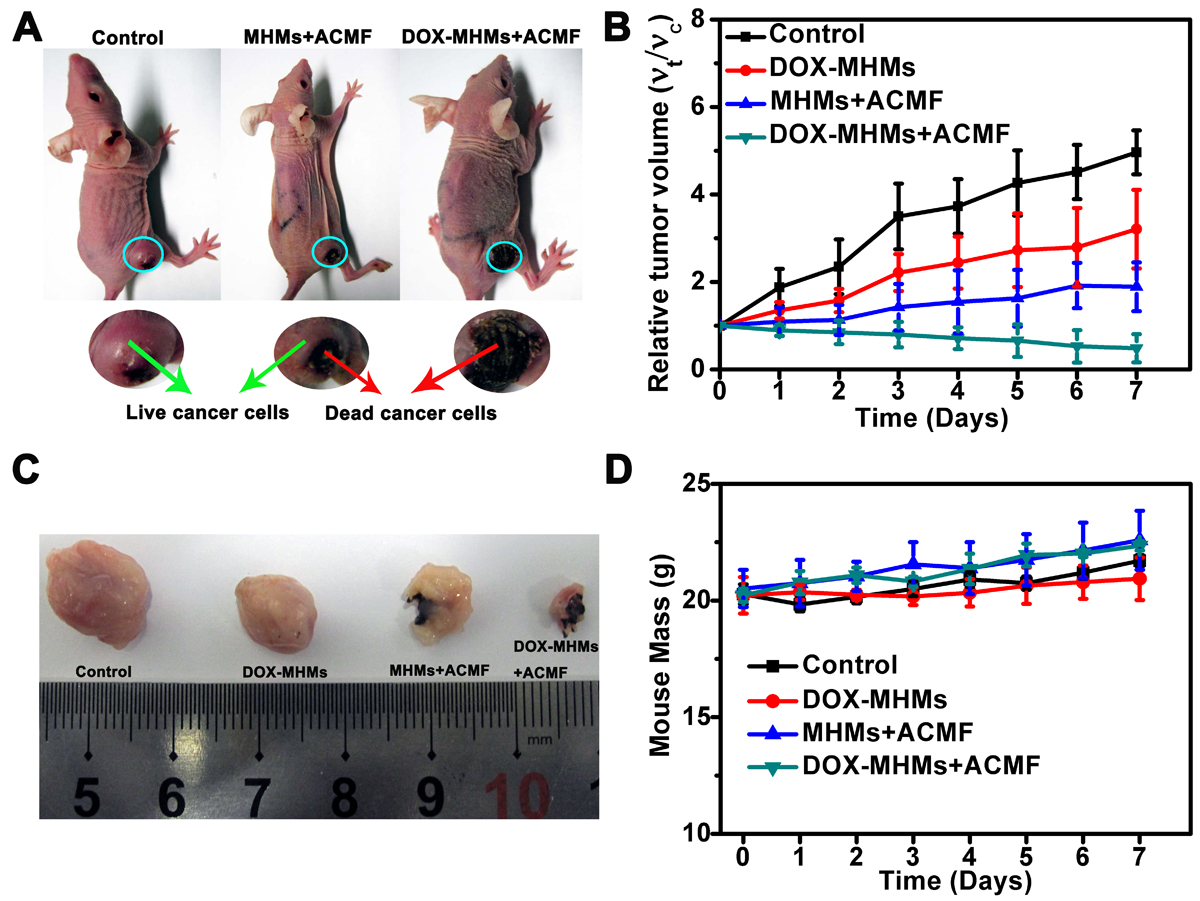
(A) 4T1 tumor treated with PBS (left), MMS (containing no DOX) with ACMF (middle)
and DOX-MMS with ACMF (right) after 7 days. (B) Tumor therapy using MMS with or
without DOX and with or without ACMF treatment for 30 min. (C) the typical photographs of
excised tumors from mice on the 7 day. (D) Mouse mass as a function of days post treatment.