磷脂膜的主相变温度对于其生物医学应用如可控药物释放等至关重要,可通过在磷脂膜中嵌入疏水性纳米颗粒调节磷脂膜的主相变温度。然而,嵌入磷脂膜的纳米颗粒的表面性质如何影响磷脂膜的主相变温度仍然不清楚。因此,我们运用粗粒度分子动力学模拟的方法来探索这一问题。结果表明纳米颗粒的表面粗糙度和表面修饰分子的密度均影响磷脂膜的主相变温度。增加纳米颗粒的表面粗糙度将提升磷脂膜的主相变温度,而增加纳米颗粒表面修饰分子的密度可以先降低后提升磷脂膜的主相变温度。我们的模拟结果很好地解释了最近的一些实验现象(White, et al. ACS Nano, 2012, 6, 4678-4685.等),并对纳米颗粒嵌入磷脂膜用于可控药物释放等方面具有启示意义。
Xubo Lin, Ning Gu*. Surface Properties of Encapsulating Hydrophobic Nanoparticles Regulates the Main Phase Transition Temperature of Lipid Bilayers: A Simulation Study. Nano Research, 2014, 7(8): 1195-1204.
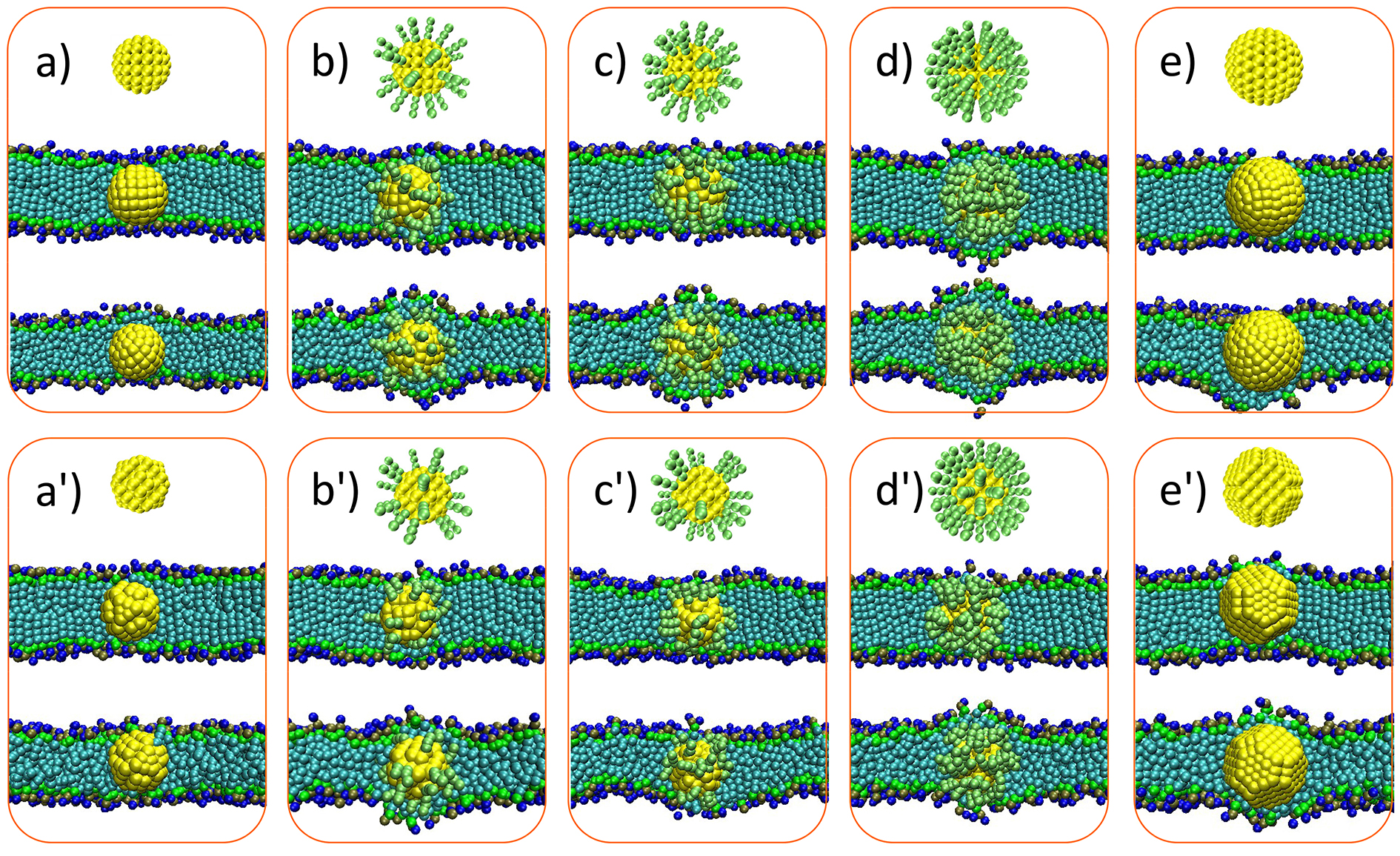
Snapshots of smooth NP of 3nm (0% ligands, a), 3nm (33%, b), 3nm (50%, c), 3nm (100%, d), 4nm (0%, e) and its encapsulation in the DPPC bilayer of gel phase (middle of orange box) and fluid phase (bottom of orange box). a')-e') are corresponding cases of rough NP similar to smooth NP.