经过多年的研究,深静脉血栓的清除仍存在诸多问题。在没有采取任何预防措施的基础上,术后深静脉形成血栓的发生率为10%到40%,尤其骨科手术后其发生率高达40%到60%。深静脉血栓的形成会导致肺高血压、血栓综合征以及致命性肺动脉栓塞等多种疾病。目前临床上使用抗凝药物如低分子量的肝素等,但是这些药物的使用在降低血栓的同时增加了高危出血和伤口并发症等风险。近年来的研究表明,具有释放一氧化氮(NO)的生物聚合物膜在抑制血栓的形成中能发挥良好的作用,然而NO在深静脉血栓的溶解方面的研究目前尚未见报道。本实验的主要目的是评价包裹NO的微气泡对大鼠深静脉血栓的促溶作用,实验结果表明,NO微气泡促深静脉溶血栓过程主要通过降低血小板和炎症细胞的聚集,增加胶原转化以及刺激内皮细胞的抗凝血功能等实现。
Chao Wang, Fang Yang, Zhihong Xu, Dongquan Shi, Dongyang Chen, Jin Dai, Ning Gu, Qing Jiang. Intravenous release of NO from lipidic microbubbles accelerates deep vein thrombosis resolution in a rat mode. Thromb Res (2012), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2012.11.002.

Fig. 1. The thrombosed animal model: (A)Abridged general view of the IVC and LCIV ligation;(B)Example of venous ligation in our surgical, mixed thrombus would present at the
segments below the ligation of the vein(arrows).
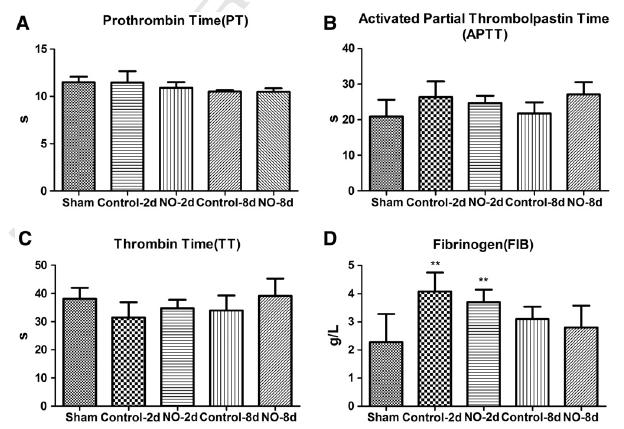
Fig. 2. Influence on coagulation function: PT, APTT, TT and FIB of peripheral blood were tested. PT(A), APTT(B), and TT(C) had no statistical difference in all groups over time; FIB(D) increased
significantly in both thrombosed groups compared with that in sham group (Pb0.05) at day 2. **Pb0.05 versus sham.
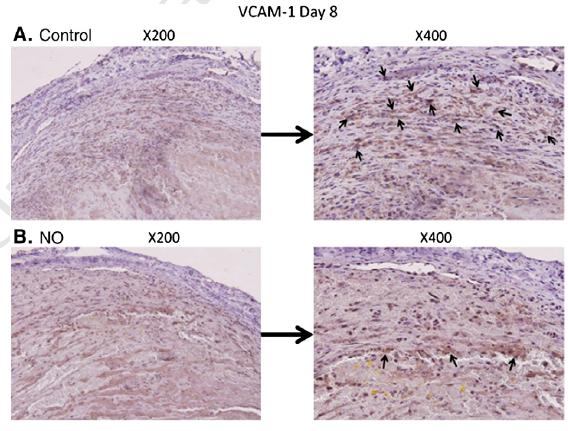
Fig. 3. Immunohistochemical staining analysis: (A) Representative immunohistochemical staining for the over-expression of VCAM-1 in control group;(B) Representative
immunohistochemical staining for the inhibition of over-expression of VCAM-1 in NO microbubbles group.