金属纳米材料中的局域表面等离激元具有许多特殊的光学性质,有着非常广泛的应用前景,是当今纳米科学研究中的一个热点。当纳米颗粒之间非常接近的时候,其相互之间的近场耦合作用会强烈的影响系统的光学特性,我们使用电磁散射理论研究了多层纳米壳链状结构的光学性质。
首先我们建立了一种通用的基于米氏(Mie)理论的多层多粒子光学散射的全解析方法,该方法能够精确的对包含任意多个同心球形粒子的系统的近场和远场光学响应进行求解。同时我们采用有限元方法的验证了程序的正确性,相比于数值方法,该方法能够大大的减少计算资源和时间。我们使用该方法计算了制备方法比较成熟的金硅金三层纳米壳的光学性质,分析了多层纳米壳中不同模式的等离激元的耦合机制。当金壳层和金核的等离激元的震荡相位相同的时候,系统的吸收和散射大大增强,我们称之为“明模式”;当金壳层和金核的等离激元的震荡相位相反的时候,会强烈的抑制散射,我们称之为“暗模式”。和原子物理中的FANO效应相似,“明模式”和“暗模式”的耦合会导致不对称的消光峰。最后我们计算了一维金属纳米壳链状结构的近场和远场响应,分析了近场耦合对“暗模式”的影响以及电磁增强效应,结果表明近场耦合效应使“明模式”的光谱峰变宽并且红移,但是对“暗模式”的影响很小,并且在“暗模式”波长下,电场增强达到最大。
Meng Wang, Min Cao, Xin Chen, and Ning Gu,
Subradiant Plasmon Modes in Multilayer Metal–Dielectric Nanoshells, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115 (43), pp 20920–20925
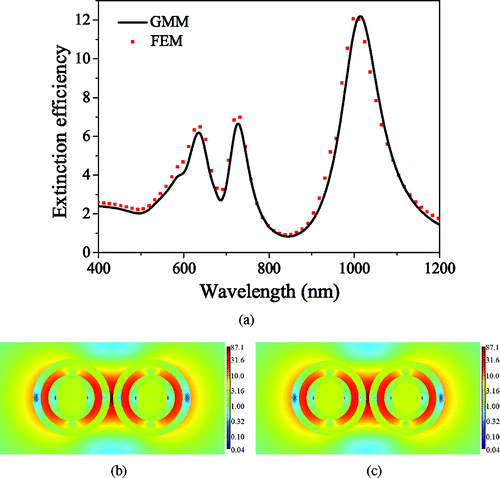
Figure 2. Comparison of the calculated extinction and near-field results of GMM theory and FEM. (a) Extinction efficiency of a R20/30/40/50 nm Au@SiO2@Au@SiO2 MNS dimer with interparticle spacing of 5 nm. Local electric fields in the x–y plane plotted in logarithmic scale calculated from FEM (b) and GMM theory (c) at the dipolar resonance wavelength (λ = 1010 nm).
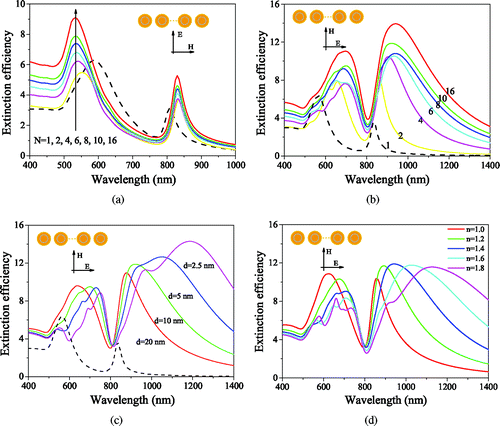
Figure 4. Extinction efficiencies of R25/30/50 nm Au@SiO2@Au MNS chains. MNSs aligned normal (a) and parallel (b) to the polarization with different particle numbers (d = 10 nm). (C) MNSs aligned parallel to the polarization with different spacings (N = 10). (d) MNS chain embedded in mediums with different refractive indices (N = 10, d = 10 nm). The dashed line corresponds to a single Au@SiO2@Au MNS.

Figure 5. Far- and near-field optical properties of a R25/30/50 nm Au@SiO2@Au MNS chain (N = 10, d = 10 nm). Optical cross sections (a), surface charge distributions (b), and electric field intensities (c) are plotted. The dashed lines in (a) correspond to a solid gold nanoparticle chain.