随着纳米材料的广泛应用,其对环境的影响也越来越重要,纳米材料的土壤环境应用研究刚刚起步,对其在土壤环境中的分配、反应、行为、归趋及生态毒理等尚缺乏系统了解。微生物在保持土壤生态系统健康和功能方面起着至关重要的作用[1,2],是氮、磷、钾、硫、磷等元素及有机残留物分解循环的关键环节,会在全球范围内影响营养和碳循环。本研究探索了氧化铁纳米颗粒对土壤微生物群落结构和尺寸的影响。结果表明纳米粒子增加了土壤细菌的丰富度,从而能够促进氮、硫和磷等元素的循环,加强有机残留物的分解能力,这些能力在植物生长中具有重要的作用,因此会对植物生长产生有益的影响。另外氧化铁纳米材料的加入并不会影响土壤细菌群落的大小,使得其生态环境保持相对的稳定。
Shiying He,Youzhi Feng,Hongxuan Ren,Yu Zhang,Ning Gu* and Xiangui Lin
The impact of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles on the soil bacterial community.J Soils Sediments (2011) 11:1408–1417

Figure 2. DGGE fingerprinting profiles of 16S rRNA gene in soils treated with different concentrations of IOMNPs (Fe3O4 and γ-Fe2O3). Sample designations are indicated above each DGGE lane. The bands excised for sequencing are circled and numbered from 1 to 12.
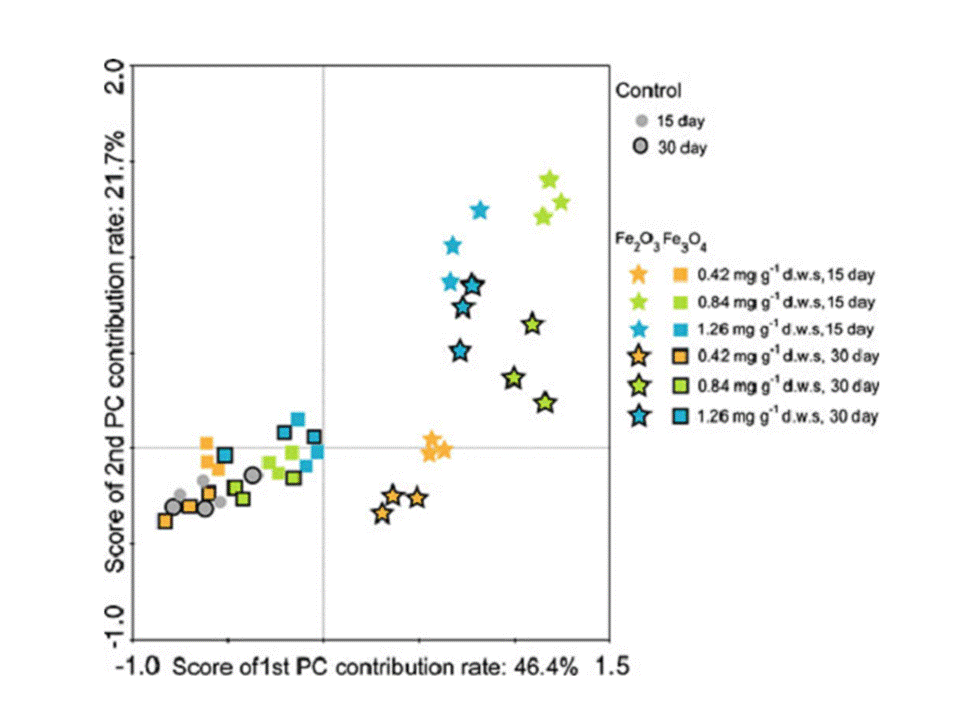
Figure 4. Principal component analysis of the 16S rRNA gene banding profiles for bacteria from the soil amended with different concentrations of IOMNPs (Fe3O4 and γ-Fe2O3). The contribution rates of the first and second principal component (PC) are 46.4% and 21.7%, respectively.
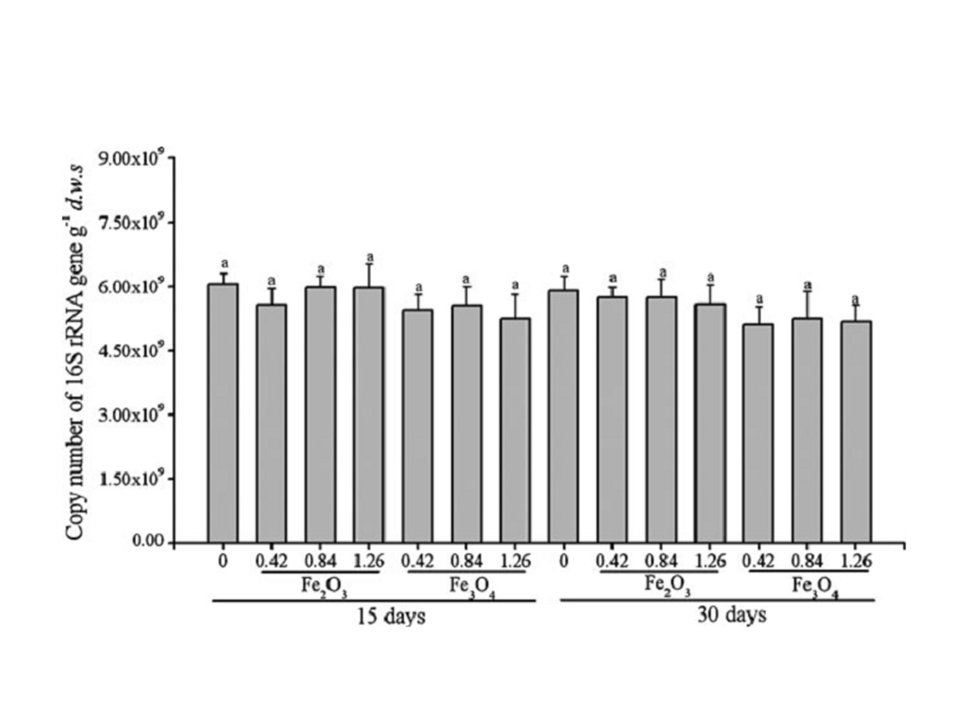
Figure 5. The copy number of 16S rRNA gene from the soil sprayed with different concentrations of IOMNPs. Data are the mean of three determinations and the error bars indicate SD. Values are representative of three independent experiments. Three replicates were used in this experiment. Groups that are significantly different are indicated by different letters (p<0 .05).
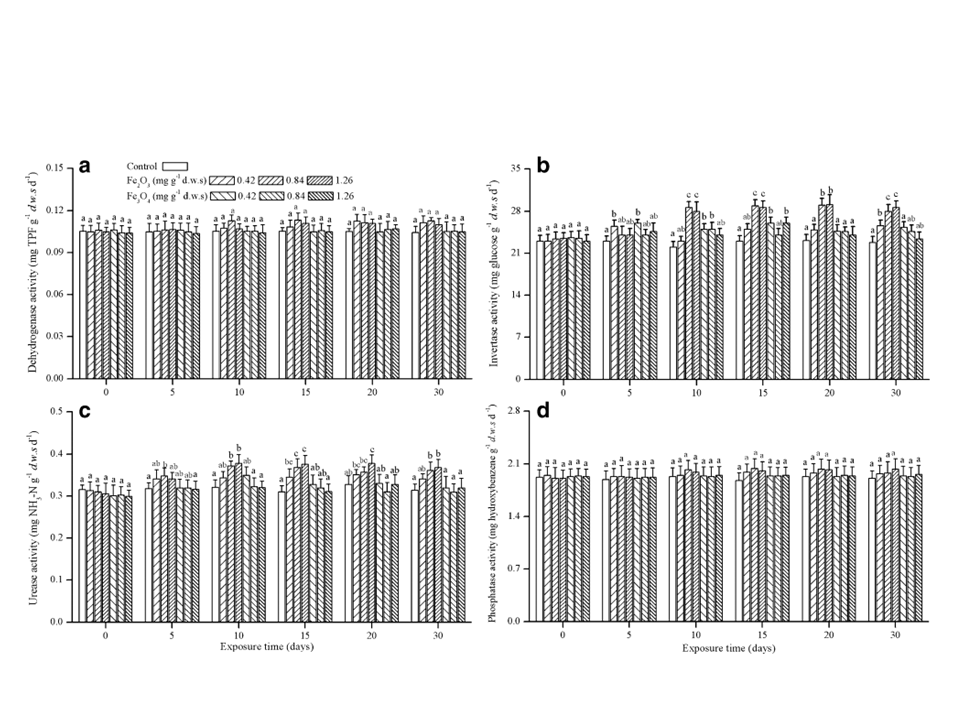
Figure 6. Enzyme activities of dehydrogenase (A), invertase (B), urease (C) and phosphatase (D) of samples treated with different concentrations of IOMNPs (Fe3O4 and γ-Fe2O3) at different intervals. Bars indicate the standard deviation of the mean. Groups that are significantly different are indicated by different letters (p<0 .05).