治疗性药物特别是抗肿瘤药物通常对正常组织和细胞具有较强的毒副作用,因此将药物靶向输送到病灶部位并缓慢释放出来,减少药物在正常组织中的分布和释放,具有重要意义。磁性聚合物微囊因其具有良好的生物安全性和磁响应性,是理想的药物载体,已成为近年来纳米医药领域研究的热点。在药物传输系统中掺入磁性纳米颗粒,可以在外加磁场的控制下,将载药系统定向输送到靶向部位,使药物在病灶部位释放。这样既能有效提高靶向性和药物利用率,还可以控制药物在正常组织中的浓度从而降低药物的毒副作用。
本文采用微乳液和层层自组装法制备了磁性海藻酸微囊,以阿霉素作为模型药物研究了磁性微囊的包封率、载药量及在交变磁场下的药物释放行为。实验结果表明,磁性海藻酸微囊的平均粒径为2.67 µm,呈超顺磁性,其饱和磁化强度为14.2 emu/g,磁含量约为30 wt%。 磁性微囊的包封率和载药量分别为56.4%和3.5%。在交变磁场作用下,磁性微囊具有良好的刺激响应释放的性能。
Jiwei Liu, Yu Zhang, Chunyu Wang, Ruizhi Xu, Zhong, Magnetically Sensitive Alginate-Templated Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Microcapsules for Controlled Release of Doxorubicin ,J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 7673–7679
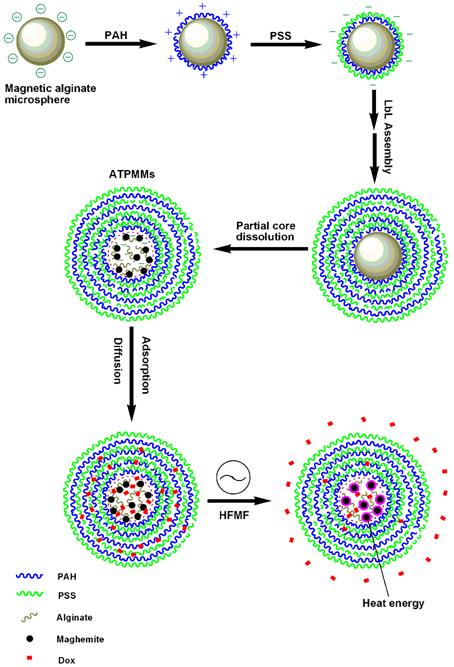
Scheme 1. Schematic illustration of the LbL process forming the ATPMMs, Dox loading and in vitro release under HFMF.
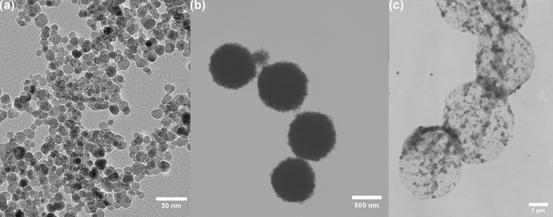
Figure 1. TEM images of the morphology of (a) DMSA-coated γ-Fe2O3 NPs, (b) magnetic alginate microspheres, and (c) ATPMMs.
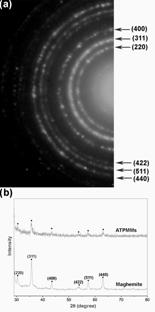
Figure 3. SAED (a) and XRD (b) patterns of the ATPMMs.

Figure 4. TGA curve of ATPMMs.
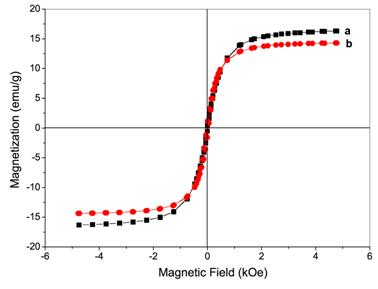
Figure 5. Room-temperature hysteresis loops of (a) magnetic alginate microspheres and (b) ATPMMs.
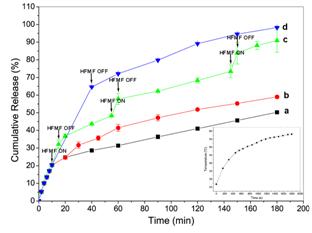
Figure 7. Drug-release profiles of ATPMMs. The samples were incubated at 25 oC (a) and 50 oC (b) in the absence of HFMF. The samples were actuated by applying the HFMF for 5 min at three specific times (c) and for duration of 30 min (d). The inset shows temperature increase curve of the ATPMMs when applying the HFMF.